Introduction
In the competitive world of kitchenware, durability, aesthetics, and food safety are top priorities for brands and retailers. Physical Vapor Deposition (PVD) coating has emerged as a game-changing surface treatment technology, offering superior performance compared to traditional plating methods.
But what exactly is PVD coating, how does it work, and why should kitchenware buyers care? This article breaks down the science, applications, benefits, and limitations of PVD—and why leading manufacturers are adopting it for high-end cookware, cutlery, and utensils.
This article explains:
✔ How PVD coating works (and why it’s superior to traditional plating)
✔ Key applications in kitchenware (with real-world examples)
✔ Benefits for retailers & brands (higher margins, lower returns)
✔ Current limitations (and emerging innovations)
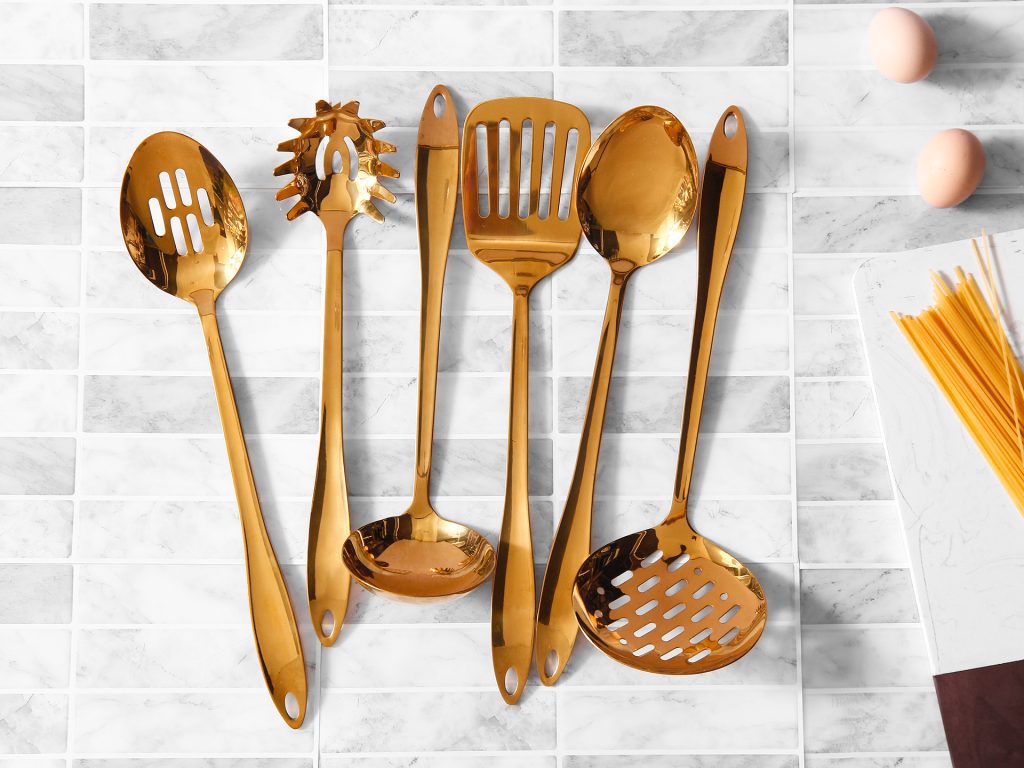

1.The Science of PVD Coating
How It Works
PVD (Physical Vapor Deposition) is a vacuum-based process where metals like titanium or chromium are vaporized and deposited as ultra-thin, ultra-hard coatings. The 3-stage process:
- Evaporation – Target material (e.g., titanium) is heated into vapor.
- Ionization – Vapor is charged into plasma for stronger bonding.
- Deposition – Particles form a micron-thick film on the substrate (e.g., stainless steel).
Key Difference vs. Electroplating:
- PVD is a dry, eco-friendly process (no toxic wastewater).
- Coatings are 3-5x harder and more adhesive.
Common PVD Types in Kitchenware
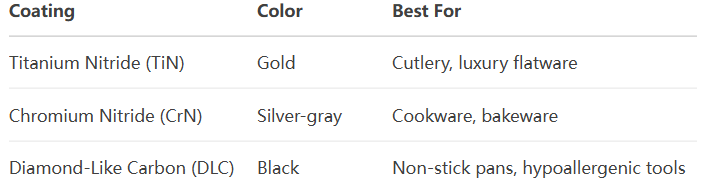

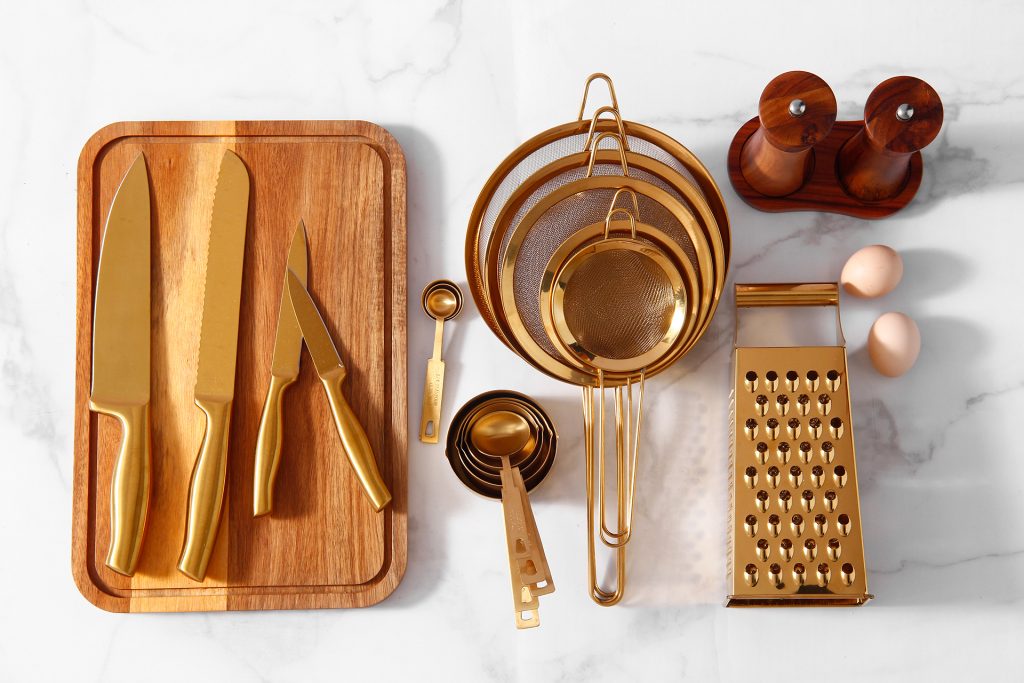
2.Why Top Brands Use PVD in Kitchenware
Proven Applications
Premium Cutlery
- PVD-coated knives retain sharpness 3x longer than uncoated blades.
- Example: Global, Wüsthof use TiN coatings for scratch-resistant finishes.
High-End Cookware
- DLC (Diamond-Like Carbon) provides PTFE-free non-stick properties.
- Resists saltwater corrosion better than ceramic coatings.
Kitchen Fixtures
- Faucets, sink handles with PVD resist fingerprints and tarnishing.
Retailer Benefits
✅ Higher price points (PVD-coated products sell at 20-30% premiums).
✅ Fewer returns due to peeling/chipping (common with electroplating).
✅ Marketing appeal (“Space-grade coating technology”).


3. Limitations & Future Trends
Challenges for Buyers
⚠️ Higher Cost – PVD adds 15-25% to manufacturing costs vs. electroplating.
⚠️ Color Limitations – Cannot achieve bright reds/blues like powder coating.
⚠️ Repair Difficulty – Damaged coatings require complete stripping.
Innovations to Watch
- Hybrid PVD-Ceramic Coatings – Enhanced non-stick performance.
- Low-Temperature PVD – Enables coating on heat-sensitive materials.
4. Key Questions for Kitchenware Buyers
When sourcing PVD-coated products, ask suppliers:
- “What’s your adhesion test method?” (Scratch tests should exceed 5N force).
- “Do you pre-treat substrates?” – Proper cleaning is critical for bond strength.
- “Can you provide FDA/LFGB compliance docs?” – Ensure food safety.


Why Follow Us?
We help brands and retailers:
✔ Supply high-quality PVD-coated kitchenware from our audited factories.
✔ Optimize cost/performance (e.g., choosing CrN vs. TiN for specific uses).
✔ Develop market-ready products with the right coatings for your audience.
✅Want to learn more about PVD applications or kitchenware sourcing?
✅ Follow us for expert insights on materials, trends, and supply chain strategies.
✅ Message us for a free “PVD Coating Buyer’s Checklist”.
Final Thought
PVD isn’t just a “premium feature”—it’s a long-term cost saver through reduced replacements and higher customer satisfaction. Brands that understand its nuances will gain a competitive edge.

